Introduction
Bees are essential to our world. They help plants grow and provide us with food by moving pollen from one flower to another. However, bees are in trouble because their homes are disappearing, harmful chemicals are used on plants, and climate change is affecting them. Understanding why bees matter and how we can help them is key to keeping our environment healthy and our food supply secure.
The Role of Bees in Pollination
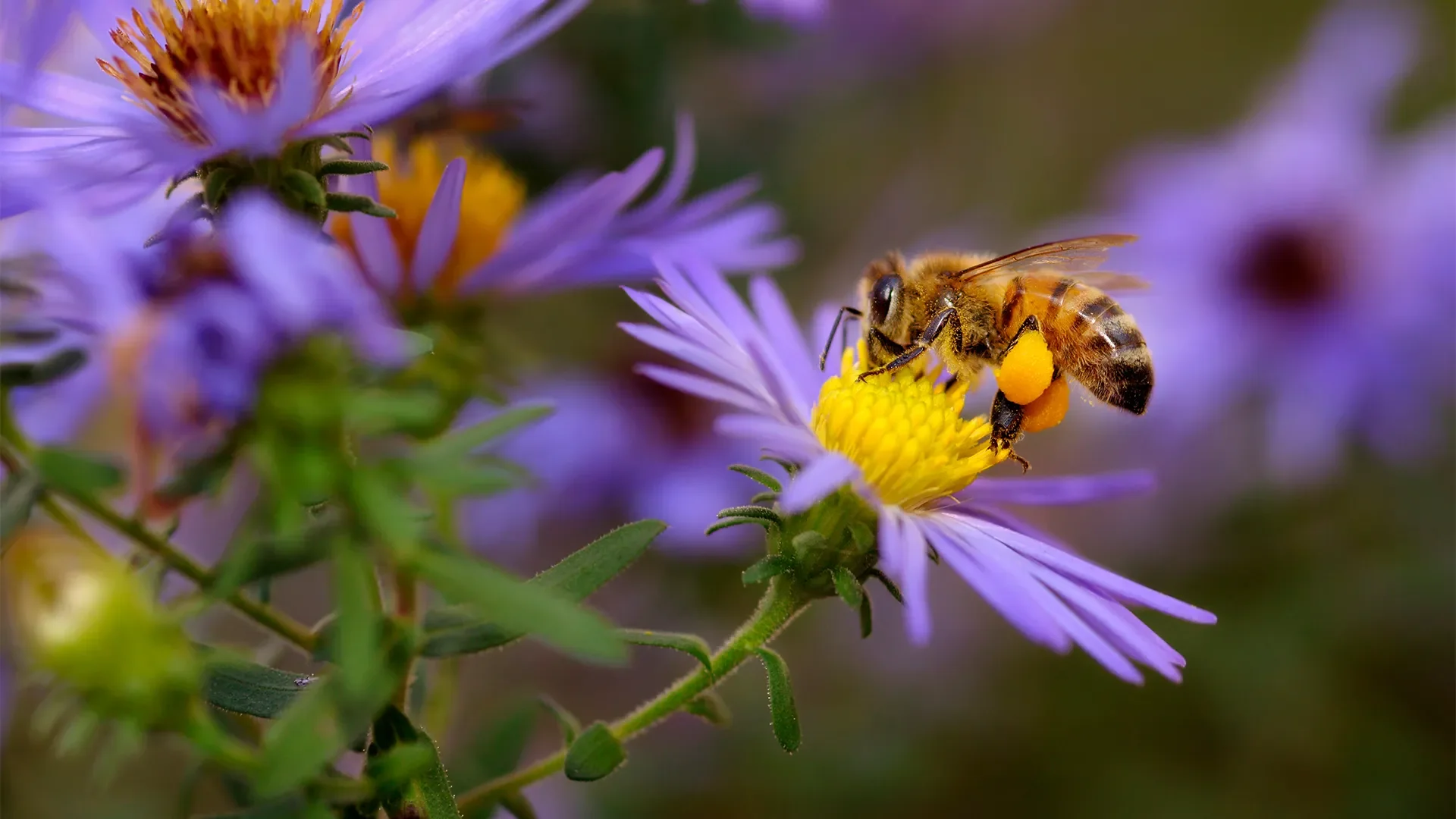
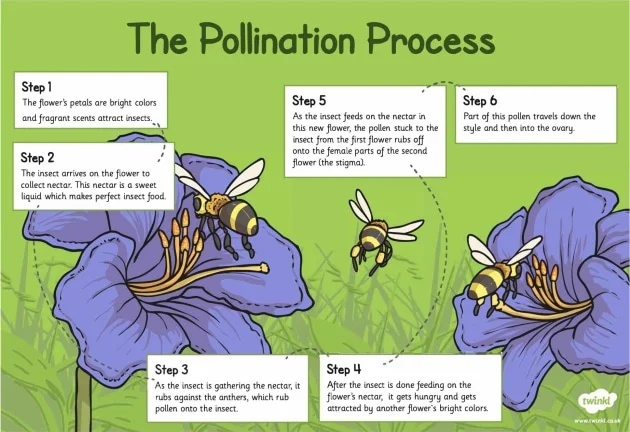
Bees are amazing pollinators, transferring pollen, which helps plants produce seeds and fruits. About 75% of the world's plants and 35% of our food crops need bees and other pollinators to grow. Fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds all rely on bees. Without them, we'd have less food and fewer flowers, impacting our diets and the beauty of nature.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Health
Bees support a wide variety of plants, ensuring biodiversity and ecosystem health. This plant diversity provides food and shelter for different animals. Without bees, many plants would struggle to reproduce, leading to fewer species and a weaker environment.
Economic Impact
Bees are incredibly valuable to agriculture. Their pollination work is worth billions of dollars each year. Crops like almonds, apples, blueberries, and cucumbers depend on bees. If bee populations continue to drop, crop yields will go down, food prices will rise, and our economy will suffer.
Threats to Bee Populations
Bees face many dangers, including loss of habitat, pesticides, diseases, parasites, and climate change. Urban development and farming reduce the number of wildflowers and nesting sites, which are essential for native species like bumble bees and solitary bees. Pesticides can poison bees or make their food unsafe, particularly affecting honey bee colonies. Diseases such as those caused by the Varroa mite and issues like colony collapse disorder also threaten European honey bee populations and contribute to the overall declining bee populations. The combined impact of these threats not only endangers bees but also affects human health due to the crucial role bees play in pollination.
How You Can Help
Plant Bee-Friendly Flowers
Grow a mix of native plants that bloom at different times of the year to provide bees with a steady food supply. This ensures that bees, including solitary bees and native species, have access to nectar and pollen throughout the seasons.
Avoid Pesticides
Use fewer chemicals in your garden and opt for natural pest control methods. Pesticides can be harmful to bees, so choosing organic or bee-friendly options can make a big difference.
Create Habitats
Provide places for bees to nest by leaving bare soil, making bee hotels, and keeping old trees and logs. These simple actions can offer bees, especially solitary bees, safe places to live and reproduce.
Support Local Beekeepers
Buy honey and other products from local beekeepers who practice sustainable beekeeping. This supports the local economy and encourages practices that are beneficial for honey bee colonies and overall bee populations.
Spread Awareness
Teach others about why bees are important and encourage bee-friendly practices in your community. By spreading knowledge, you can help create a more bee-friendly world, ensuring the protection of both honey bees and native species.
How Bees Impact Global Food Security
Bees play a crucial role in global food security. They are responsible for pollinating a significant portion of the crops that we rely on for our daily nutrition. Foods such as almonds, apples, blueberries, and cucumbers are just a few examples of crops that depend on bee pollination. Without bees, the availability and variety of these foods would diminish, leading to potential food shortages and higher prices.
Moreover, honey bees contribute to the pollination of many plants that are used for livestock feed. This means that a decline in bee populations can also affect the meat and dairy industries, as the animals would have less food to eat. In this way, bees are indirectly responsible for a substantial part of our diet, even for those who do not consume plant-based foods directly.
The Interconnectedness of Bees and Other Pollinators
While bees are among the most well-known pollinators, they are not the only ones. Other insects like butterflies, beetles, and flies, as well as birds and bats, also contribute to pollination. However, bees are particularly efficient pollinators due to their behavior and anatomy. They are uniquely adapted to collect and transfer pollen, which makes them especially important for the pollination of many crops.
By protecting honey bees, we also help other pollinators. The measures we take to create bee-friendly environments, such as planting diverse flowers and reducing pesticide use, benefit all pollinators. This creates a more resilient and productive ecosystem, ensuring that plants have multiple pollinators to rely on.
The Importance of Wild Bees
While managed honeybee colonies are crucial for agriculture, wild bees are equally important. There are over 20,000 species of wild bees, and they often specialize in pollinating specific plants. This specialization can make wild bees more effective pollinators for certain crops compared to honeybees.
Wild bees also provide essential services in natural ecosystems. They help maintain the health of wild plants, which in turn support a variety of wildlife. Protecting wild bees involves conserving their natural habitats and ensuring they have access to food sources year-round.
The Importance of Honey Bees
Honeybees are crucial to our ecosystem and agriculture for several reasons. First, they are highly efficient pollinators, responsible for pollinating around 75% of the fruits, vegetables, and nuts we consume. This includes essential crops like apples, almonds, blueberries, and cucumbers. Their pollination not only ensures a diverse food supply but also supports the production of seeds and fruits, which are vital for plant reproduction and biodiversity. Honey bees also contribute to the economy, with their pollination services valued at billions of dollars annually. Without them, crop yields would decrease, leading to higher food prices and potential shortages. Additionally, honey bees produce honey, beeswax, and other products that have significant economic and cultural value. They also help maintain healthy ecosystems by supporting the growth of wild plants, which provide food and habitat for other wildlife. In summary, honey bees are indispensable for food security, economic stability, and environmental health.
Steps to Create a Bee-Friendly Community
Creating a bee-friendly community requires collective effort. Here are some steps that communities can take to support bees:
- Community Gardens: Establish community gardens with a variety of bee-friendly plants. These gardens can serve as educational sites where people learn about bees and sustainable gardening practices.
- Pesticide Regulations: Advocate for local regulations that limit the use of harmful pesticides. Communities can work together to promote the use of organic and bee-safe products.
- Bee Conservation Programs: Support or start conservation programs that focus on protecting and restoring bee habitats. These programs can include initiatives like planting wildflowers along roadsides and creating urban green spaces.
- Public Education Campaigns: Raise awareness about the importance of bees through public education campaigns. Use social media, local events, and school programs to spread the message.
- Support Local Farmers and Beekeepers: Encourage the community to buy products from local farmers and beekeepers. This not only supports the local economy but also promotes sustainable agricultural practices.
Community Education and Involvement
Workshops and Classes: Organize workshops and classes on beekeeping, pollinator-friendly gardening, and the importance of bees. These can help educate the community on how to create and maintain environments that support bee health.
Bee Habitat Initiatives
Pollinator Pathways: Develop and maintain "pollinator pathways" in urban and suburban areas. These are corridors of bee-friendly plants that connect parks, gardens, and green spaces, allowing bees to travel safely and access food sources.
Residential Involvement: Encourage residents to participate by planting bee-friendly flowers in their yards and gardens. Provide information on the best plants for local bees and how to maintain them.
Policy and Advocacy
Bee-Friendly Legislation: Lobby for local ordinances that protect pollinator habitats and limit pesticide use. Advocate for policies that support sustainable farming practices and the protection of natural habitats.
Funding and Grants: Secure funding and grants for bee conservation projects. These can come from government programs, non-profit organizations, and private donors dedicated to environmental preservation.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Local Businesses: Partner with local businesses to sponsor bee-friendly initiatives. This could include funding for community gardens, educational programs, or conservation projects.
Research Institutions: Collaborate with universities and research institutions to monitor bee populations and study the effectiveness of conservation efforts. Use this data to inform and improve community practices.
By taking these additional steps, communities can create a more supportive environment for bees, ensuring their survival and the continued health of our ecosystems.
The Future of Honey Bees and Our Responsibility
The future of honey bees is in our hands. Our actions today will determine whether bee populations recover or continue to decline. By understanding the vital role that bees play in our ecosystem and taking proactive steps to protect them, we can ensure a healthier and more sustainable future.
Investing in research is also critical. Scientists are continuously studying bee behavior, health, and ecology to develop better conservation strategies. Supporting this research can lead to innovative solutions that protect bees and, by extension, our food supply and natural environment.
Conclusion
Bees are essential for our environment, food production, and economy. By learning about their importance and taking steps to protect them, we can ensure a healthier and more sustainable future. Small actions, like planting flowers, avoiding pesticides, and supporting local beekeepers, can make a big difference in protecting bee populations and, in turn, our world.